
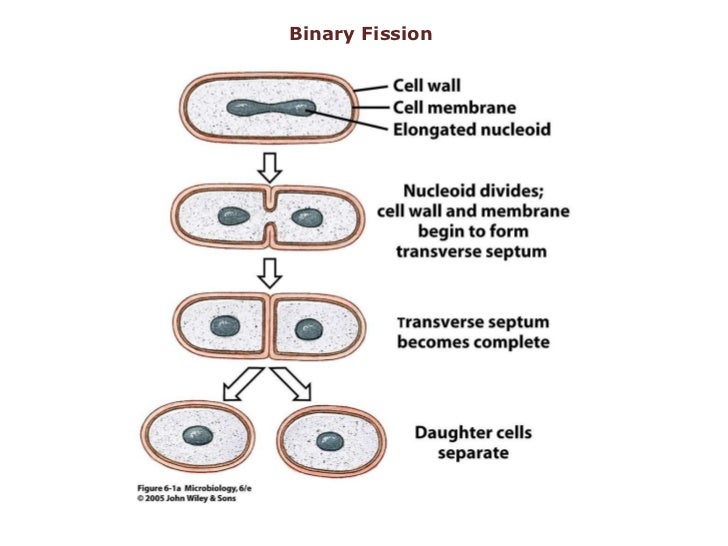
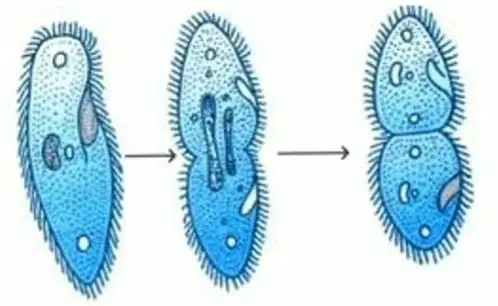
Figure: Bacterial Growth Curve: This chart shows the logarithmic growth of bacteria. In autecological studies, bacterial growth in batch culture can be modeled with four different phases: lag phase, exponential or log phase, stationary phase, and death phase. The basic means requires bacterial enumeration (cell counting) by direct and individual (microscopic, flow cytometry), direct and bulk (biomass), indirect and individual (colony counting), or indirect and bulk (most probable number, turbidity, nutrient uptake) methods. The measurement of an exponential bacterial growth curve in batch culture was traditionally a part of the training of all microbiologists. If the number surviving exceeds unity on average, the bacterial population undergoes exponential growth. The doubling time is the generation time of the bacteria. Both daughter cells from the division do not necessarily survive. Therefore, “local doubling” of the bacterial population occurs. Providing no mutational event occurs the resulting daughter cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Many endospore-producing bacteria are nasty pathogens, for example Bacillus anthracis, the cause of anthrax.\)īacterial growth is the division of one bacterium into two daughter cells in a process called binary fission. This makes destroying them very difficult. These are dormant structures, which are extremely resistant to hostile physical and chemical conditions such as heat, UV radiation and disinfectants. That’s why we can quickly become ill when pathogenic microbes invade our bodies. After one more hour the number of bacteria will have risen to a colossal 16,777,216. This means that in just seven hours one bacterium can generate 2,097,152 bacteria. When conditions are favourable such as the right temperature and nutrients are available, some bacteria like Escherichia coli can divide every 20 minutes. Each daughter cell is a clone of the parent cell. The bacterial cell then elongates and splits into two daughter cells each with identical DNA to the parent cell. Binary fission begins when the DNA of the bacterium divides into two (replicates). In this process the bacterium, which is a single cell, divides into two identical daughter cells.

Most bacteria reproduce by binary fission. © gaetan stoffel / iStockģD illustration of Escherichia coli How do bacteria reproduce? Relatively few bacteria are parasites or pathogens that cause disease in animals and plants. Some types cause food spoilage and crop damage but others are incredibly useful in the production of fermented foods such as yoghurt and soy sauce. Some bacteria live in the soil or on dead plant matter where they play an important role in the cycling of nutrients. A lot of these bacterial cells are found lining the digestive system. There are approximately 10 times as many bacterial cells as human cells in the human body. Some live in or on other organisms including plants and animals including humans. © ttsz / iStockīacteria are found in every habitat on Earth: soil, rock, oceans and even arctic snow. They can exist as single cells, in pairs, chains or clusters. For example it may contain a gene that makes the bacterium resistant to a certain antibiotic.īacteria are classified into five groups according to their basic shapes: spherical (cocci), rod (bacilli), spiral (spirilla), comma (vibrios) or corkscrew (spirochaetes). The plasmid often contains genes that give the bacterium some advantage over other bacteria. Some bacteria have an extra circle of genetic material called a plasmid rather than a nucleus. Their control centre, containing the genetic information, is contained in a single loop of DNA. Bacteria are microbes with a cell structure simpler than that of many other organisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
